自定义View 测量过程(Measure)
前言
- 自定义
View是Android开发者必须了解的基础 - 网上有大量关于自定义
View原理的文章,但存在一些问题:内容不全、思路不清晰、无源码分析、简单问题复杂化 等 - 今天,我将全面总结自定义View原理中的
measure过程,我能保证这是市面上的最全面、最清晰、最易懂的
Carson带你学Android自定义View文章系列:
Carson带你学Android:自定义View基础
Carson带你学Android:自定义View-ViewRoot、DecorView、Window区别是什么
Carson带你学Android:一文梳理自定义View工作流程
Carson带你学Android:自定义View绘制准备-DecorView创建
Carson带你学Android:自定义View Measure过程
Carson带你学Android:带你了解神秘的MeasureSpec类
Carson带你学Android:自定义View Layout过程
Carson带你学Android:自定义View Draw过程
Carson带你学Android:手把手教你写一个完整的自定义View
Carson带你学Android:Canvas类全面解析
Carson带你学Android:Path类全面解析
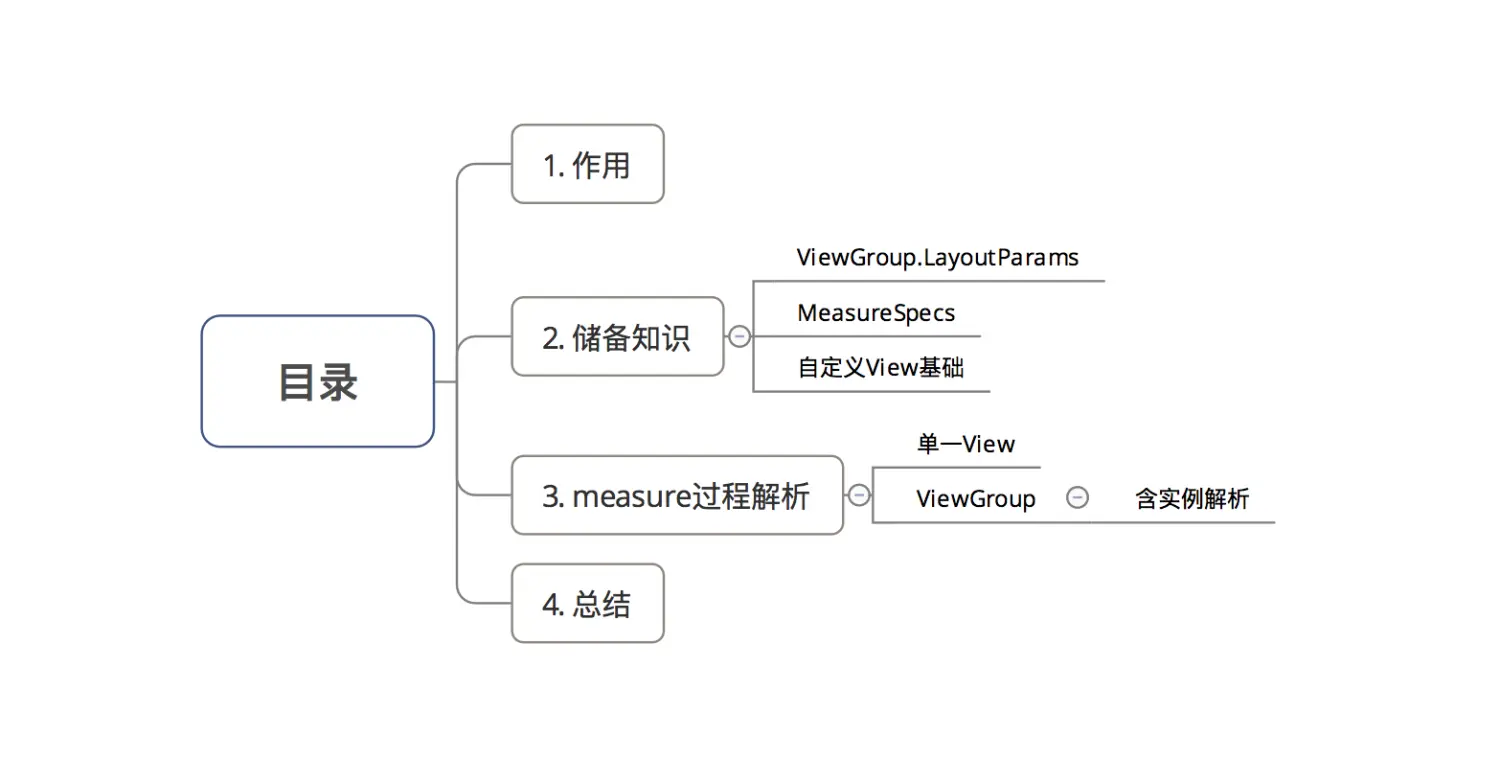
目录
示意图
1. 作用
测量View的宽 / 高
- 在某些情况下,需要多次测量
(measure)才能确定View最终的宽/高;- 该情况下,
measure过程后得到的宽 / 高可能不准确;- 此处建议:在
layout过程中onLayout()去获取最终的宽 / 高
2. 储备知识
了解measure过程前,需要3个储备知识:
- 自定义
View基础知识 ViewGroup.LayoutParams类()MeasureSpecs类
2.1 最基本的知识储备
具体请看文章:> 自定义View基础
2.2 ViewGroup.LayoutParams
- 简介
布局参数类
ViewGroup的子类(RelativeLayout、LinearLayout)有其对应的ViewGroup.LayoutParams子类- 如:
RelativeLayout的ViewGroup.LayoutParams子类
=RelativeLayoutParams
作用
指定视图View的高度(height)和 宽度(width)等布局参数。具体使用
通过以下参数指定
| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| 具体值 | dp / px |
| fill_parent | 强制性使子视图的大小扩展至与父视图大小相等(不含 padding ) |
| match_parent | 与fill_parent相同,用于Android 2.3 & 之后版本 |
| wrap_content | 自适应大小,强制性地使视图扩展以便显示其全部内容(含 padding ) |
1
2
3
4
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //自适应大小
android:layout_height="match_parent" //与父视图等高
android:layout_height="fill_parent" //与父视图等高
android:layout_height="100dip" //精确设置高度值为 100dip
- 构造函数
构造函数 =View的入口,可用于初始化 & 获取自定义属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// View的构造函数有四种重载
public DIY_View(Context context){
super(context);
}
public DIY_View(Context context,AttributeSet attrs){
super(context, attrs);
}
public DIY_View(Context context,AttributeSet attrs,int defStyleAttr ){
super(context, attrs,defStyleAttr);
// 第三个参数:默认Style
// 默认Style:指在当前Application或Activity所用的Theme中的默认Style
// 且只有在明确调用的时候才会生效,
}
public DIY_View(Context context,AttributeSet attrs,int defStyleAttr ,int defStyleRes){
super(context, attrs,defStyleAttr,defStyleRes);
}
// 最常用的是1和2
}
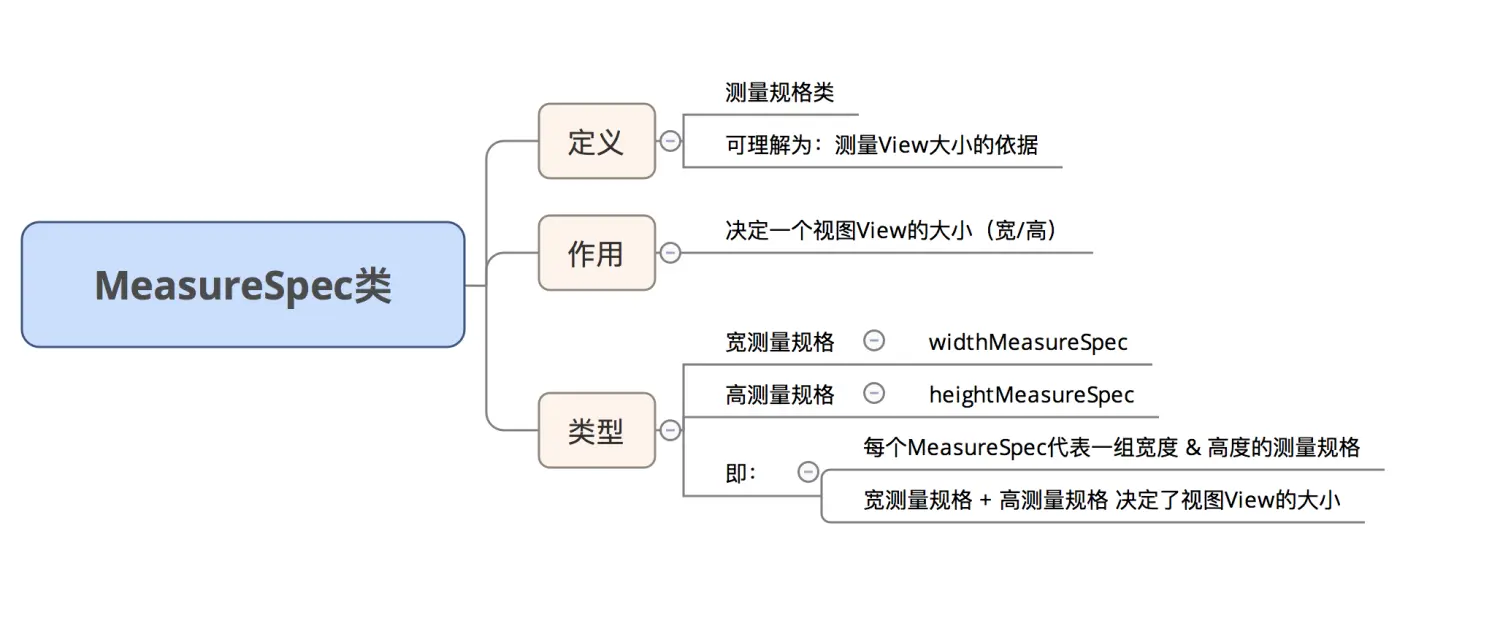
2.3 MeasureSpec
示意图
具体请看文章:Android自定义View基础:MeasureSpec类到底是什么?
3. measure过程详解
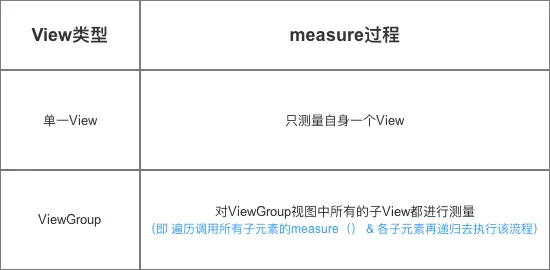
measure过程 根据View的类型分为2种情况:
示意图
接下来,我将详细分析这两种measure过程
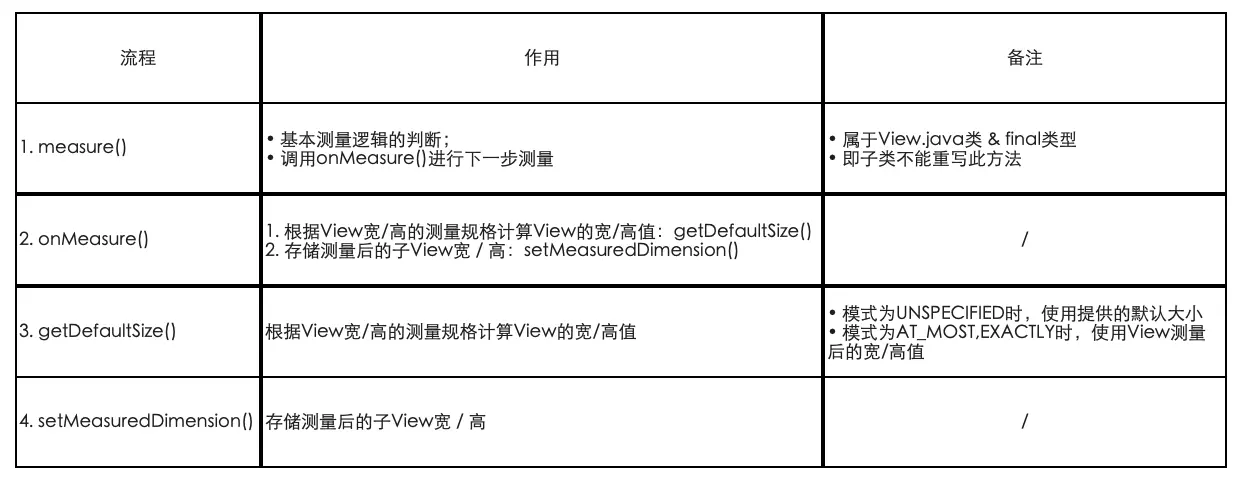
3.1 单一View的measure过程
应用场景
在无现成的控件View满足需求、需自定义单一View时。
- 如:制作一个支持加载网络图片的
ImageView控件- 注:自定义
View在多数情况下都有替代方案:图片 / 组合动画,但二者可能会导致内存耗费过大,从而引起内存溢出等问题。
具体流程
单一View的measure过程
源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
/**
* 源码分析:measure()
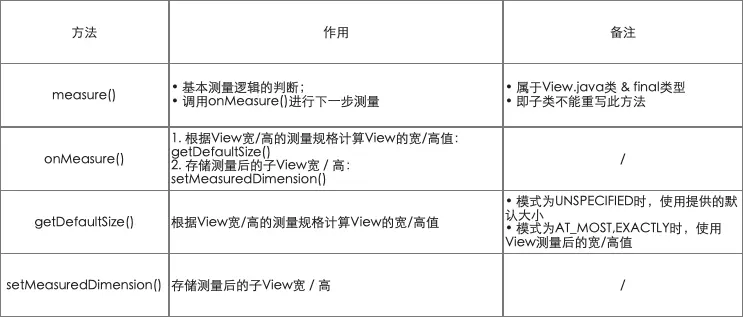
* 定义:Measure过程的入口;属于View.java类 & final类型,即子类不能重写此方法
* 作用:基本测量逻辑的判断
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 参数说明:View的宽 / 高测量规格
...
int cacheIndex = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ? -1 :
mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 计算视图大小 ->>分析1
} else {
...
}
/**
* 分析1:onMeasure()
* 作用:a. 根据View宽/高的测量规格计算View的宽/高值:getDefaultSize()
* b. 存储测量后的View宽 / 高:setMeasuredDimension()
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 参数说明:View的宽 / 高测量规格
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
// setMeasuredDimension() :获得View宽/高的测量值 ->>分析2
// 传入的参数通过getDefaultSize()获得 ->>分析3
}
/**
* 分析2:setMeasuredDimension()
* 作用:存储测量后的View宽 / 高
* 注:该方法即为我们重写onMeasure()所要实现的最终目的
*/
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
//参数说明:测量后子View的宽 / 高值
// 将测量后子View的宽 / 高值进行传递
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
// 由于setMeasuredDimension()的参数是从getDefaultSize()获得的
// 下面继续看getDefaultSize()的介绍
/**
* 分析3:getDefaultSize()
* 作用:根据View宽/高的测量规格计算View的宽/高值
*/
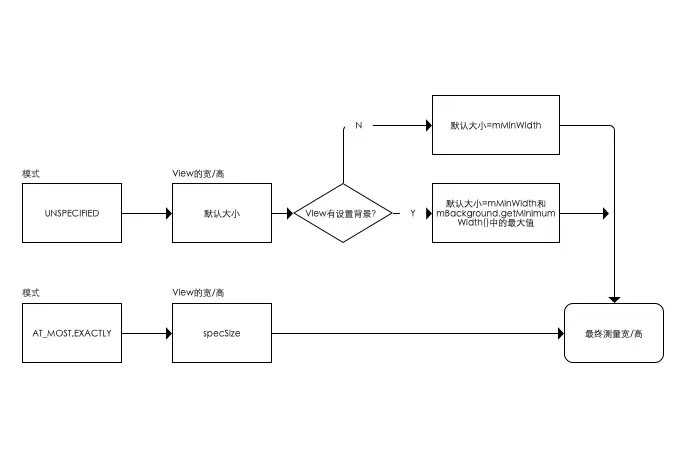
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
// 参数说明:
// size:提供的默认大小
// measureSpec:宽/高的测量规格(含模式 & 测量大小)
// 设置默认大小
int result = size;
// 获取宽/高测量规格的模式 & 测量大小
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
// 模式为UNSPECIFIED时,使用提供的默认大小 = 参数Size
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
// 模式为AT_MOST,EXACTLY时,使用View测量后的宽/高值 = measureSpec中的Size
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
// 返回View的宽/高值
return result;
}
上面提到,当测试规格的模式(mode)是UNSPECIFIED时,使用的是提供的默认大小(即getDefaultSize()的第一个参数size)。那么,提供的默认大小具体是多少呢?
答:getSuggestedMinimumWidth() / getSuggestedMinimumHeight()。具体请看下面源码分析。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth,mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
// 逻辑说明
// 1. 若View无设置背景,那么View的宽度 = mMinWidth
// 即android:minWidth属性所指定的值,若无指定则为0.
// 2. 若View设置了背景,View的宽度为mMinWidth和mBackground.getMinimumWidth()中的最大值
// 下面继续看mBackground.getMinimumWidth()的源码分析
/**
* mBackground.getMinimumWidth()源码分析
*/
public int getMinimumWidth() {
final int intrinsicWidth = getIntrinsicWidth();
// 即mBackground.getMinimumWidth()的大小 = 背景图Drawable的原始宽度
return intrinsicWidth > 0 ? intrinsicWidth :0 ;
// 若无原始宽度,则为0;
}
至此,单一View的宽/高值已经测量完成,即对于单一View的measure过程已经完成。
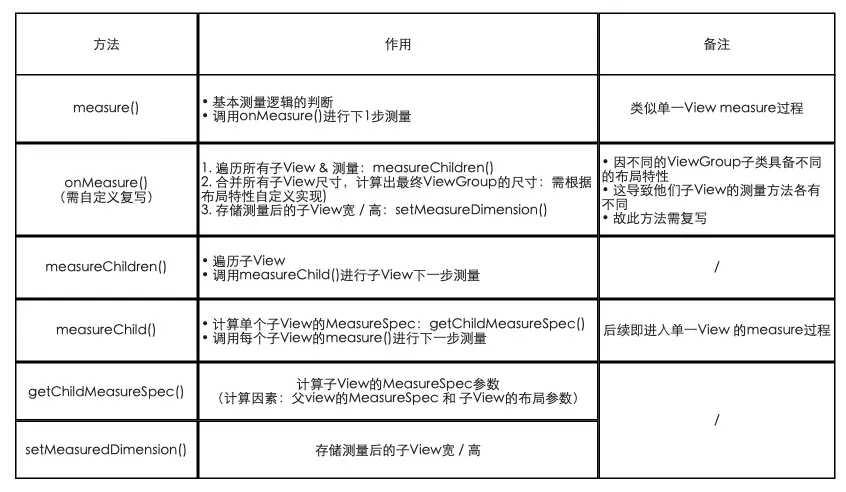
源码总结
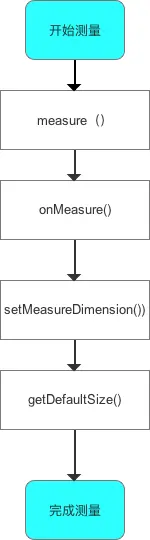
对于单一View的测量流程(Measure)各个方法说明如下所示。
测量宽高的关键在于getDefaultSize(),该方法的测量逻辑如下图所示。
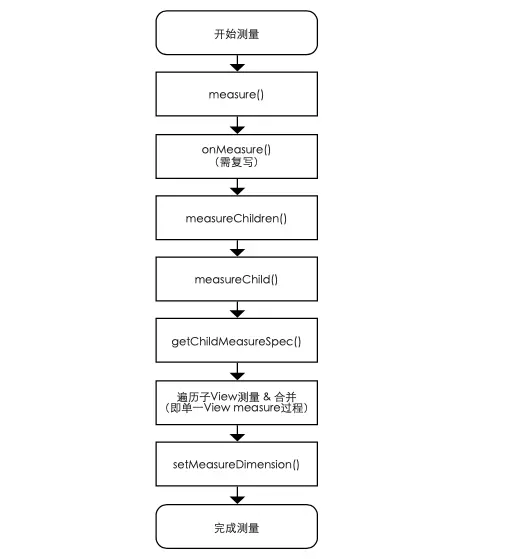
3.2 ViewGroup的measure过程
应用场景
利用现有的多个组件根据特定的布局方式组成一个新的组件(即包含多个子View)。
如:底部导航条中的条目,一般都是上图标(ImageView)、下文字(TextView),那么这两个就可以用自定义ViewGroup组合成为一个Veiw,提供两个属性分别用来设置文字和图片,使用起来会更加方便。
示意图
测量原理
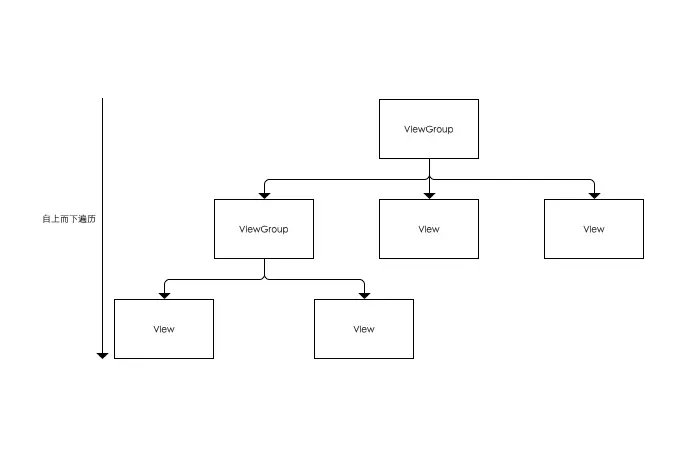
从ViewGroup至子View、自上而下遍历进行(即树形递归),通过计算整个ViewGroup中各个View的属性,从而最终确定整个ViewGroup的属性。即:
- 遍历测量所有子View的尺寸(宽/高);
- 合并所有子View的尺寸(宽/高),最终得到ViewGroup父视图的测量值。
具体流程
需要特别注意的是:若需进行自定义ViewGroup,则需重写onMeasure(),在下面的章节会详细讲解。
源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* 源码分析:measure()
* 作用:
* 1. 基本测量逻辑的判断;
* 2. 调用onMeasure()
* 注:与单一View measure过程中讲的measure()一致
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 仅展示核心代码
// ...
int cacheIndex = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ? -1 :
mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// 调用onMeasure()计算视图大小 -> 分析1
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
// ...
}
/**
* 分析1:onMeasure()
* 作用:遍历子View &测量
* 注:ViewGroup = 一个抽象类 = 无重写View的onMeasure(),需自身复写
**/
根据上一小节可知,单一View的measure过程对onMeasure()有统一的实现(如下代码),但为什么ViewGroup的measure过程没有呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/**
* onMeasure()
* 作用:a. 根据View宽/高的测量规格计算View的宽/高值:getDefaultSize()
* b. 存储测量后的View宽 / 高:setMeasuredDimension()
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 参数说明:View的宽 / 高测量规格
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
// setMeasuredDimension() :获得View宽/高的测量值 ->>分析2
// 传入的参数通过getDefaultSize()获得 ->>分析3
}
原因是:onMeasure()方法的作用是测量View的宽/高值,而不同的ViewGroup(如LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、自定义ViewGroup子类等)具备不同的布局特性,这导致它们的子View测量方法各有不同,所以onMeasure()的实现也会有所不同。
因此,ViewGroup无法对onMeasure()作统一实现。这个也是单一View的measure过程与ViewGroup的measure过程最大的不同。
复写onMeasure()
针对Measure流程,自定义ViewGroup的关键在于:根据需求复写onMeasure(),从而实现子View的测量逻辑。复写onMeasure()的步骤主要分为三步:
- 遍历所有子View及测量:measureChildren()
- 合并所有子View的尺寸大小,最终得到ViewGroup父视图的测量值:需自定义实现
- 存储测量后View宽/高的值:setMeasuredDimension()
具体如下所示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//仅展示关键代码
...
// 步骤1:遍历所有子View & 测量 -> 分析1
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 步骤2:合并所有子View的尺寸大小,最终得到ViewGroup父视图的测量值
void measureCarson{
... // 需自定义实现
}
// 步骤3:存储测量后View宽/高的值
setMeasuredDimension(widthMeasure, heightMeasure);
// 类似单一View的过程,此处不作过多描述
}
/**
* 分析1:measureChildren()
* 作用:遍历子View & 调用measureChild()进行下一步测量
*/
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 参数说明:父视图的测量规格(MeasureSpec)
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
// 遍历所有子view
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
// 调用measureChild()进行下一步的测量 ->分析2
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
/**
* 分析2:measureChild()
* 作用:1. 计算单个子View的MeasureSpec
* 2. 测量每个子View最后的宽 / 高:调用子View的measure()
*/
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
// 1. 获取子视图的布局参数
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 2. 根据父视图的MeasureSpec & 布局参数LayoutParams,计算单个子View的MeasureSpec
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
// 3. 将计算好的子View的MeasureSpec值传入measure(),进行最后的测量
// 下面的流程即类似单一View的过程,此处不作过多描述
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
至此,ViewGroup的measure过程分析完毕
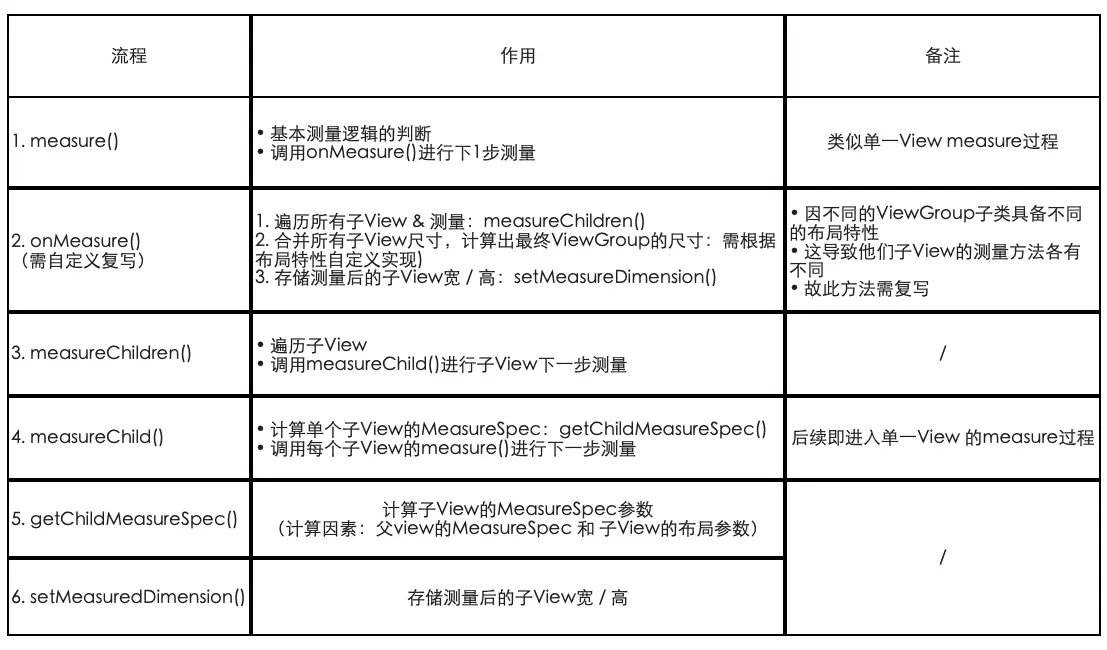
流程总结
对于视图组ViewGroup的测量流程(Measure)各个方法说明总结如下所示。
为了让大家更好地理解ViewGroup的measure过程(特别是复写onMeasure()),下面,我将用ViewGroup的子类LinearLayout来分析下ViewGroup的measure过程
实例解析
为了更好理解ViewGroup的measure过程(特别是复写onMeasure()),本小节将用ViewGroup的子类LinearLayout来分析ViewGroup的measure过程。
此处主要分析的是LinearLayout的onMeasure(),具体如下所示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 根据不同的布局属性进行不同的计算
// 此处只选垂直方向的测量过程,即measureVertical() ->分析1
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
/**
* 分析1:measureVertical()
* 作用:测量LinearLayout垂直方向的测量尺寸
*/
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 获取垂直方向上的子View个数
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
// 遍历子View获取其高度,并记录下子View中最高的高度数值
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
// 子View不可见,直接跳过该View的measure过程,getChildrenSkipCount()返回值恒为0
// 注:若view的可见属性设置为VIEW.INVISIBLE,还是会计算该view大小
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
// 记录子View是否有weight属性设置,用于后面判断是否需要二次measure
totalWeight += lp.weight;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
// 如果LinearLayout的specMode为EXACTLY且子View设置了weight属性,在这里会跳过子View的measure过程
// 同时标记skippedMeasure属性为true,后面会根据该属性决定是否进行第二次measure
// 若LinearLayout的子View设置了weight,会进行两次measure计算,比较耗时
// 这就是为什么LinearLayout的子View需要使用weight属性时候,最好替换成RelativeLayout布局
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
skippedMeasure = true;
} else {
int oldHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// 步骤1:该方法内部最终会调用measureChildren(),从而 遍历所有子View & 测量
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec,totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
...
}
// 步骤2:合并所有子View的尺寸大小,最终得到ViewGroup父视图的测量值(需自定义实现)
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 1. mTotalLength用于存储LinearLayout在竖直方向的高度
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
// 2. 每测量一个子View的高度, mTotalLength就会增加
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin +
lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
// 3. 记录LinearLayout占用的总高度
// 即除了子View的高度,还有本身的padding属性值
mTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
int heightSize = mTotalLength;
// 步骤3:存储测量后View宽/高的值
setMeasureDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth,width))
...
}
至此,对于自定义View流程中最重要、最复杂的测量流程(measure)分析完毕。
4. 总结
- 测量流程(Measure)根据视图(View)的类型分为两种情况:单一View和视图组ViewGroup;
- 二者最大的区别在于:单一View的measure过程对onMeasure()有作统一实现,而ViewGroup的Measuer过程没有;
- 具体测量流程总结如下所示
- Carson带你学Android自定义View文章系列:
Carson带你学Android:自定义View基础
Carson带你学Android:自定义View-ViewRoot、DecorView、Window区别是什么
Carson带你学Android:一文梳理自定义View工作流程
Carson带你学Android:自定义View绘制准备-DecorView创建
Carson带你学Android:自定义View Measure过程
Carson带你学Android:带你了解神秘的MeasureSpec类
Carson带你学Android:自定义View Layout过程
Carson带你学Android:自定义View Draw过程
Carson带你学Android:手把手教你写一个完整的自定义View
Carson带你学Android:Canvas类全面解析
Carson带你学Android:Path类全面解析
欢迎关注Carson_Ho的简书
不定期分享关于安卓开发的干货,追求短、平、快,但却不缺深度。
请点赞!因为你的鼓励是我写作的最大动力!
本文转自 https://www.jianshu.com/p/1dab927b2f36,如有侵权,请联系删除。